3.7.24. Automaton with same input symbol
A constraint for which the catalogue provides an automaton belonging to the following category:
Symbols of the alphabet are split in two categories: neutral ones and non-neutral ones.
Non-neutral symbols correspond to symbols occurring on transitions between two distinct states, while neutral symbols correspond to all the other symbols of the alphabet.
Self-loops labelled by a neutral symbol do not modify any counter.
Ignoring transitions labelled by neutral symbols, every state has its incoming transitions labelled by the same non-neutral symbol.
Ignoring transitions labelled by neutral symbols, outgoing transitions of a state are not labelled by the symbol associated with its incoming non-loop transitions.
For such automata we define the semantics of a state as the regular expression associated with the language fragment obtained from entering state to just before leaving state .
Figure 3.7.6. Semantics of the states of the automaton of the constraint
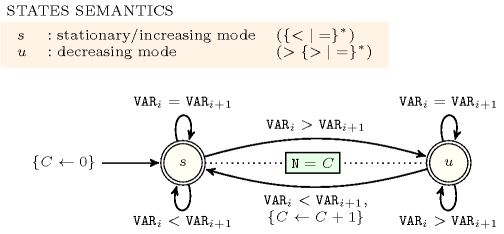
As an example, consider the constraint and its automaton depicted by Figure 3.7.6. The alphabet corresponds to the set of symbols from which and are non-neutral symbols (i.e., the symbols associated with the transitions between states and ), and is a neutral symbol. First there is no counter modification on all self-loops. If we remove the self-loops carrying the neutral symbol we have that:
All incoming transitions in state are labelled by the non-symbol , and all outgoing transitions from state are not labelled by .
All incoming transitions in state are labelled by the non-symbol , and all outgoing transitions from state are not labelled by .
The corresponding state semantics is given by the upper-leftmost box.