5.109. dag
| DESCRIPTION | LINKS | GRAPH |
- Origin
- Constraint
- Argument
- Restrictions
- Purpose
Consider a digraph described by the collection. Select a subset of arcs of so that the corresponding graph does not contain any circuit.
- Example
-
The constraint holds since the collection depicts a graph without circuit.
- Typical
- Symmetry
Items of are permutable.
- Algorithm
A filtering algorithm for the constraint is given in [Dooms06]. It removes potential arcs that would create a circuit of mandatory arcs.
- See also
- Keywords
- Arc input(s)
- Arc generator
-
- Arc arity
- Arc constraint(s)
- Graph property(ies)
-
- Arc input(s)
- Arc generator
-
- Arc arity
- Arc constraint(s)
- Graph property(ies)
-
- Graph model
The first graph constraint removes the loop of each vertex. The second graph constraint forbids the creation of circuits involving more than one vertex.
Part (A) of Figure 5.109.1 shows the initial graph associated with the second graph constraint of the Example slot. This initial graph from which we start is derived from the set associated with each vertex. Each set describes the potential values of the attribute of a given vertex. Part (B) of Figure 5.109.1 gives the final graph associated with the Example slot.
Figure 5.109.1. Initial and final graph of the set constraint
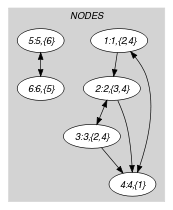
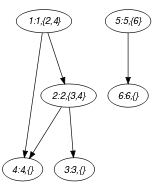
(a) (b)