5.243. max_n
| DESCRIPTION | LINKS | GRAPH |
- Origin
- Constraint
- Arguments
- Restrictions
- Purpose
is the maximum value of rank (i.e., the largest distinct value, identical values are merged) of the collection of domain variables . The maximum value has rank 0.
- Example
-
The constraint holds since its first argument is fixed to the second (i.e., ) largest distinct value of the collection .
- Typical
- Symmetries
Items of are permutable.
One and the same constant can be added to as well as to the attribute of all items of .
- Arg. properties
Functional dependency: determined by and .
- Algorithm
- Reformulation
The constraint enforces to be assigned one of the values of . The constraint provides a hand on the number of distinct values assigned to the variables of . By associating to each variable of the collection a rank variable with the reified constraint , the inequality , and by creating for each pair of variables the reified constraints
,
,
,
one can reformulate the constraint in term of reified constraints.
- See also
-
generalisation: (absolute maximum replaced by maximum or order ).
- Keywords
characteristic of a constraint: rank, maximum.
constraint arguments: pure functional dependency.
- Arc input(s)
- Arc generator
-
- Arc arity
- Arc constraint(s)
- Graph property(ies)
-
- Graph model
Parts (A) and (B) of Figure 5.243.1 respectively show the initial and final graph associated with the Example slot. Since we use the graph property, the vertex of rank 1 (without considering the loops) of the final graph is outlined with a thick circle.
Figure 5.243.1. Initial and final graph of the constraint
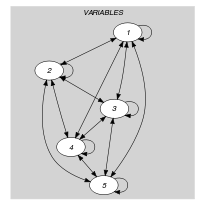
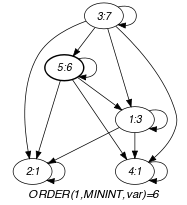
(a) (b)