5.152. equal_sboxes
| DESCRIPTION | LINKS | LOGIC |
- Origin
Geometry, derived from [RandellCuiCohn92]
- Constraint
- Synonym
.
- Types
- Arguments
- Restrictions
- Purpose
Holds if, for each pair of objects , , and coincide exactly with respect to a set of dimensions depicted by . and are objects that take a shape among a set of shapes. Each shape is defined as a finite set of shifted boxes, where each shifted box is described by a box in a -dimensional space at a given offset (from the origin of the shape) with given sizes. More precisely, a shifted box is an entity defined by its shape id , shift offset , and sizes . Then, a shape is defined as the union of shifted boxes sharing the same shape id. An object is an entity defined by its unique object identifier , shape id and origin .
Two objects and object are equal with respect to a set of dimensions depicted by if and only if, for all shifted box associated with there exists a shifted box such that, for all dimensions , (1) the origins of and coincide and, (2) the ends of and also coincide.
- Example
-
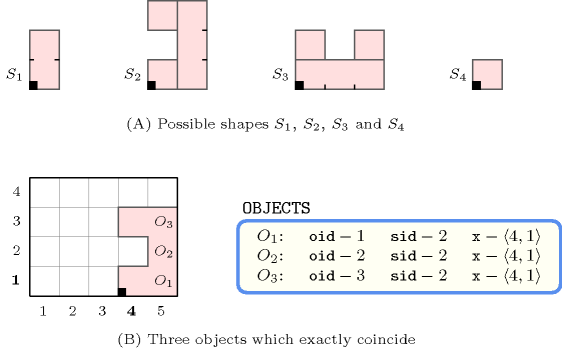
Figure 5.152.1 shows the objects of the example. Since these objects coincide exactly the constraint holds.
Figure 5.152.1. (B) The three mutually coinciding objects , , of the Example slot respectively assigned shape ; (A) shapes , , and are respectively made up from 1, 3, 3 and 1 disjoint shifted box.
- Typical
- Symmetries
Items of are permutable.
Items of are permutable.
Items of , and are permutable (same permutation used).
- Arg. properties
Suffix-contractible wrt. .
- Remark
One of the eight relations of the Region Connection Calculus [RandellCuiCohn92]. The constraint is a restriction of the original relation since it requires to have exactly the same partition between the different objects.
- See also
common keyword: , , , , , (rcc8), (geometrical constraint,logic), (rcc8).
- Keywords
- Logic