5.304. orchard
| DESCRIPTION | LINKS | GRAPH |
- Origin
- Constraint
- Arguments
- Restrictions
- Purpose
Orchard problem [Jackson1821]:
“Your aid I want, Nine trees to plant, In rows just half a score, And let there be, In each row, three—Solve this: I ask no more!”
- Example
-
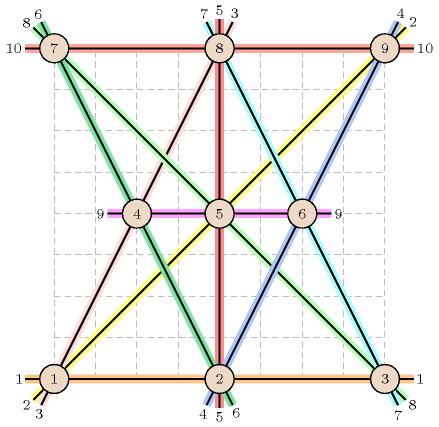
The 10 alignments of 3 trees correspond to the following triples of trees: , , , , , , , , , . Figure 5.304.1 shows the 9 trees and the 10 alignments corresponding to the example.
Figure 5.304.1. Nine trees with 10 alignments of 3 trees
- Typical
- Symmetries
Items of are permutable.
Attributes of are permutable w.r.t. permutation (permutation applied to all items).
One and the same constant can be added to the attribute of all items of .
One and the same constant can be added to the attribute of all items of .
- Arg. properties
Functional dependency: determined by .
- Keywords
characteristic of a constraint: hypergraph.
constraint arguments: pure functional dependency.
- Arc input(s)
- Arc generator
-
- Arc arity
- Arc constraint(s)
- Graph property(ies)
-
- Graph model
The arc generator with an arity of three is used in order to generate all the arcs of the directed hypergraph. Each arc is an ordered triple of trees. We use the restriction in order to generate a single arc for each set of three trees. This is required, since otherwise we would count more than once a given alignment of three trees. The formula used within the arc constraint expresses the fact that the three points of respective coordinates , and are aligned. It corresponds to the development of the expression: